OpenShift EUS-to-EUS Upgrade
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Upgrade procedure
- Inspect the current version
- Update OLM operators from initial version
- Update channel
- Check upgrade path
- Pause worker Machine Config Pool
- Update control plane to intermediate version
- Update OLM Operators in intermediate version
- Acknowledge of changes between Kubernetes APIs
- Upgrade control plane to target version
- Upgrade OLM Operators to target version
- Unpause worker MCP
- Summary
- Resources
Introduction
This article tries to cover the understanding of OpenShift EUS versions, and how to upgrade a cluster from one EUS version to the next one in a detailed procedure.
The life cycle management of a cluster in a production environment it is a very important topic, eventually all the components of our cluster are software, and those are constantly changing during the time, fixing bugs, improving features or adding new ones. Hence it is important to keep our environment updated and do that in a consistent way that avoid any service disruption.
What are EUS versions
Extended Update Support (EUS) is applied only to the even-numbered OpenShift versions like 4.12, 4.14, 4.16 and so on. Red Hat is adding an additional 6 months support to these versions.
This is convenient to avoid too many maintenance activities on our cluster, taking in account that a new Kubernetes and OpenShift version is released each 4 months, hence the EUS versions allow to skip one intermediate version to keep a cycle of two versions per year, with an extra time to schedule the upgrade, keeping an EUS version supported for 2 years.
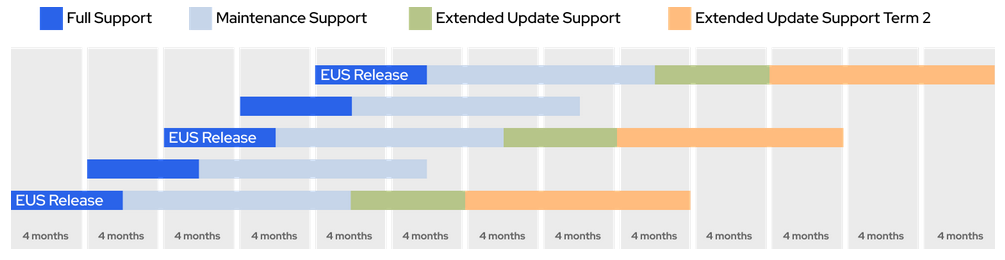
You can consult the OpenShift life cycle policy in this article.
Understanding the OpenShift life cycle management
There are two main concepts in OpenShift that we need to understand very well before move forward:
Cluster Operators: In OpenShift all the components of the Control Plane (etcd, scheduler, api, etc) are pods running in the cluster, not like a vanilla Kubernetes, that the Control Plane components can run as a systemd service on the Control plane nodes, or as Containers, but these are not Kubernetes objects itself. These pods are handled by operators called Cluster Operators (these operators are different from the OLM operators). Hence to upgrade the Control Plane of an OpenShift cluster we have to upgrade the Cluster Operators that handle these components. During the procedure described below we are going to monitor the status of the Cluster Operators in the upgrade process.
Red Hat CoreOS: The operating system running on each node of an OpenShift cluster is called Red Hat CoreOS (RHCOS). This is an immutable OS, which doesn’t allow manual changes, anything you want to configure on each node required of a MachineConfig object in the cluster, and the Machine Config Operator (which is a Cluster Operator) will make the change on the designed group of nodes within a Machine Config Pool. Also it is important to understand that each OpenShift version come with a specific version of RHCOS, this way we always know the kernel version and which packages are installed in each node, based on the OpenShift version of the cluster. Understand this is important, because during the process the nodes are rebooted to apply the rendered MachineConfig with the new RHCOS version and the required configurations.
For futher information about the upgrade process you can take a look to the OpenShift official documentaion.
Environment used for this article
To write this article a baremetal cluster with 5 nodes has been used. Three nodes as Control Plane nodes (non-schedulables), and two workers. The initial version of the cluster is OCP 4.14.16 and the target version for the upgrade is 4.16.8. Also we are going to use the MetalLB Operator as reference on how to upgrade OLM operators. This operator has the approval as Manual, in order to keep the control of when the operator is upgraded.
Upgrade procedure
Let’s get our hand dirty starting the procedure! During the procedure I’m going to explain how to do it with the CLI, sometimes I will add some screenshots of the Web Console for better understanding, but all these steps can bee done via the Web Console as well. I think it is always better to do it manually when you want to have a more detailed understanding of what is going on during each step. The OpenShift Web Console is awesome, but for learning have a lot of black magic under the hood to make our life easier.
Inspect the current version
First of all let’s review the initial status of our cluster.
We can review the current version and the nodes list of our cluster with the below command.
$ oc get clusterversion,nodes
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS
clusterversion.config.openshift.io/version 4.14.16 True False 20h Cluster version is 4.14.16
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node/master0.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
node/master1.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
node/master2.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
node/worker0.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
node/worker1.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
As you can see in the output of the above command we start on the version 4.14.16, and we have a Multi Node OpenShift with three Control Plane nodes as non-schedulables, and two workers. All of the nodes with the Kubelet version v1.27.10+c79e5e2.
Also let’s take a look to the previously mentioned Cluster Operators, to review the current status and versions.
$ oc get co
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE
authentication 4.14.16 True False False 20h
baremetal 4.14.16 True False False 20h
cloud-controller-manager 4.14.16 True False False 21h
cloud-credential 4.14.16 True False False 21h
cluster-autoscaler 4.14.16 True False False 20h
config-operator 4.14.16 True False False 20h
console 4.14.16 True False False 20h
control-plane-machine-set 4.14.16 True False False 20h
csi-snapshot-controller 4.14.16 True False False 20h
dns 4.14.16 True False False 20h
etcd 4.14.16 True False False 20h
image-registry 4.14.16 True False False 20h
ingress 4.14.16 True False False 96m
insights 4.14.16 True False False 20h
kube-apiserver 4.14.16 True False False 20h
kube-controller-manager 4.14.16 True False False 20h
kube-scheduler 4.14.16 True False False 20h
kube-storage-version-migrator 4.14.16 True False False 19h
machine-api 4.14.16 True False False 20h
machine-approver 4.14.16 True False False 20h
machine-config 4.14.16 True False False 89m
marketplace 4.14.16 True False False 20h
monitoring 4.14.16 True False False 88m
network 4.14.16 True False False 20h
node-tuning 4.14.16 True False False 20h
openshift-apiserver 4.14.16 True False False 20h
openshift-controller-manager 4.14.16 True False False 20h
openshift-samples 4.14.16 True False False 20h
operator-lifecycle-manager 4.14.16 True False False 20h
operator-lifecycle-manager-catalog 4.14.16 True False False 20h
operator-lifecycle-manager-packageserver 4.14.16 True False False 20h
service-ca 4.14.16 True False False 20h
storage 4.14.16 True False False 20h
As you can see all the Cluster Operators are in the version 4.14.16, with status AVAILABLE to True and DEGRADED to False. This is an important command to verify the health or our cluster. So right now we can say that our cluster is healthy on version 4.14.16.
Also we mentioned above that the nodes are manged by the Machine Config Operator, so let’s take a look to the current Machine Config Pools.
$ oc get mcp
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE
master rendered-master-3be71a1eb50a0fbbcea03dc72b613c54 True False False 3 3 3 0 21h
worker rendered-worker-25e7f5222944b2572fe43be49cdde9d0 True False False 2 2 2 0 21h
As expected we have two Machine Config Pools, one to manage the Control Plane nodes called master, and another to apply the configs to the Worker nodes, called worker. Highlight the current status, which is UPDATED is True and UPDATING and DEGRADED False, which means that all the Machine Config have been applied correctly to all the nodes on all the Machine Config Pools.
NOTE: I want to highlight a common misunderstanding with the nodes and the Machine Config Pools. Each node can be part only of one Machine Config Pool, for which a render of the required configuration is generated and applied by the Machine Config Operator. The nodes are part of a Machine Config Pool based on the labels of the nodes. It is important to understand that, because if we want to run a Canary upgrade, we can create new custom MCP, and sometimes is confusing how it works. The use of custom MCP is out of the scope of this article, but you can refer to the official documentation for more info about it.
Update OLM operators from initial version
Ok, at this point we have reviewed the current status of our cluster, and we have ensured that it is healthy in the expected version. Now, as a good practice, we are going to upgrade to the latest version of the OLM operators within the 4.14.16.
For this article we have configured the MetalLB Operator with the approval as Manual, in order to show each step for better understanding for the reader. So, the first thing is to see if there is a newer version of the MetalLB Operator to be approved. Let’s run the below command:
$ oc get installplan -n metallb-system | egrep 'APPROVED|false'
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED
install-mbl5p metallb-operator.v4.14.0-202408081513 Manual false
We can see in the last colum from the output above, that the install-plan require to be approved. Let’s approve it:
$ oc patch installplan -n metallb-system install-mbl5p --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"approved":true}}'
installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-mbl5p patched
Ok now let’s see if the MetalLB Operator has been updated checking the status of the Cluster Service Version object.
$ oc -n metallb-system get csv
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
metallb-operator.v4.14.0-202408081513 MetalLB Operator 4.14.0-202408081513 Succeeded
Great! We can see that the PHASE is Succeeded. Let’s move forward.
Update channel
As we want to update the the 4.16 EUS version, we have to update the channel used by the Cluster Version Operator.
First, we are going to check the current channel.
$ oc get clusterversion version -o json | jq '.spec.channel'
"eus-4.14"
Now let’s update the channel and review that the changes have been applied correctly.
$ oc adm upgrade channel eus-4.16
$ oc get clusterversion version -o json | jq '.spec.channel'
"eus-4.16"
Also we can check it from the OpenShift Web Console within the Administration > Cluster Settings. We should see somthin like below screenshot.
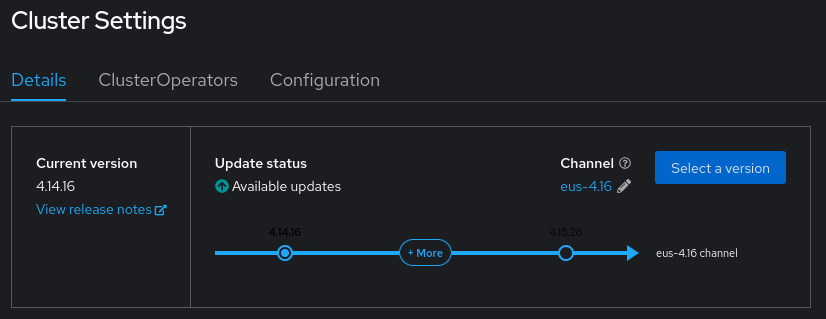
Done.
Check upgrade path
Red Hat has this web where we can check the upgrade path recommended (a Red Hat account is required to access to this resource).
We can fill the current channel as eus-4.16 and the current version and target version to generate the upgrade path recommended.
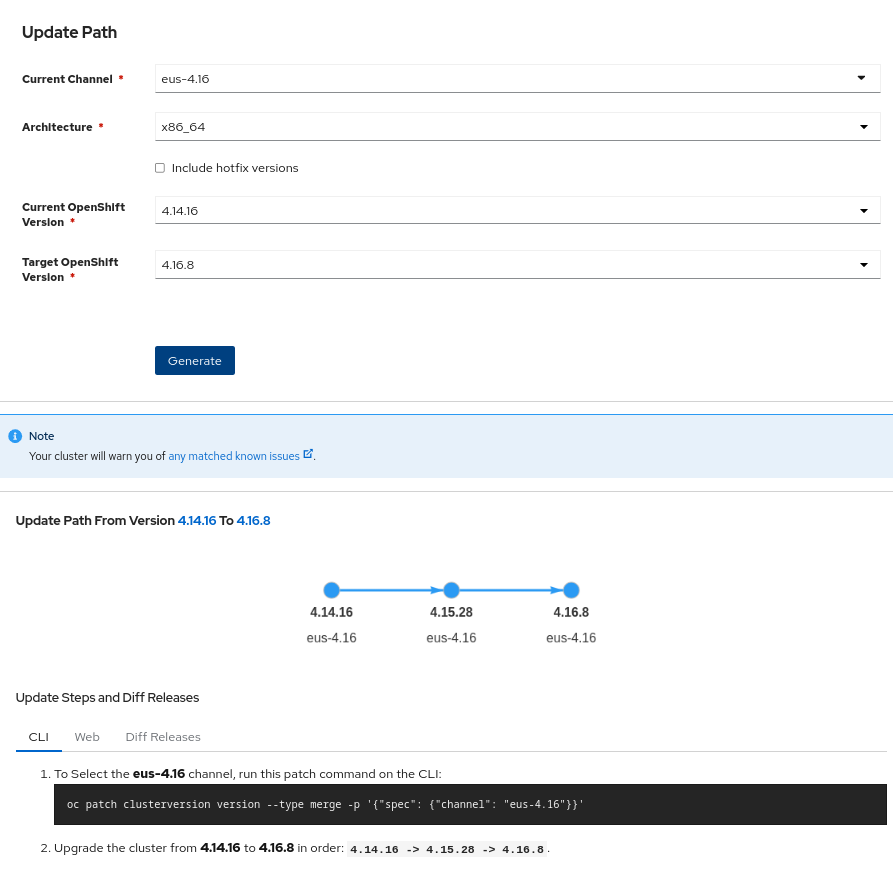
The upgrade path recommended is to upgrade first to OCP 4.15.28, afterward upgrade tp 4.16.8, and explain which command you have to run to get that.
Pause worker Machine Config Pool
In order to update only the Control Plane to the intermediate version, and keep the worker nodes running to no affect our workloads, we are going to pause the worker Machine Config Pool. This way when we start the upgrade process, only the Control Plane nodes will be upgraded and the worker nodes will keep the current version, until we get the target version of the Control Plane.
To pause the worker MCP we have to run the below command:
$ oc patch mcp/worker --patch '{"spec":{"paused":true}}' --type=merge
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/worker patched
Update control plane to intermediate version
Now we have all ready to start the first upgrade to the intermediate version 4.15.28 only on the Control Plane, this is something important to be understood, with this step none of the workloads running on the worker nodes will be affected, this step will affect only to the access of the OpenShift Control Plane.
To launch the upgrade run the below command.
oc adm upgrade --allow-explicit-upgrade --force=true --to-image=quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release:4.15.28-x86_64 --allow-upgrade-with-warnings
The above command could be more simple, but to add additional resources to this content I have decided to add a command line with more options that can be used on specific use case where the happy path is not an option.
We can check the progress of the cluster upgrade with below command:
$ oc get clusterversion
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS
version 4.14.16 True True 9m12s Working towards 4.15.28: 4 of 873 done (0% complete
Also we can look at the Web Console, within the Administration > Cluster Settings menu, and we will see something like the below screenshot.
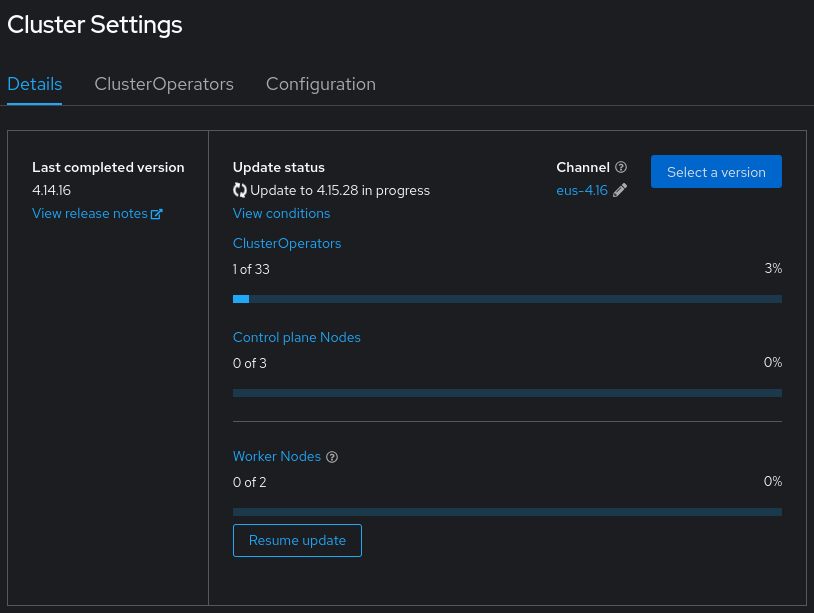
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, the components of the Control Plane are the Cluster Operators, so also we can track the status of the Cluster Operators and see how these operators are upgraded.
$ oc get co
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE
authentication 4.14.16 True False False 22h
baremetal 4.14.16 True False False 23h
cloud-controller-manager 4.14.16 True False False 23h
cloud-credential 4.14.16 True False False 23h
cluster-autoscaler 4.14.16 True False False 23h
config-operator 4.15.28 True False False 23h
console 4.14.16 True False False 22h
control-plane-machine-set 4.14.16 True False False 23h
csi-snapshot-controller 4.14.16 True False False 23h
dns 4.14.16 True False False 23h
etcd 4.15.28 True False False 23h
image-registry 4.14.16 True False False 22h
ingress 4.14.16 True False False 3h48m
insights 4.14.16 True False False 23h
kube-apiserver 4.14.16 True True False 23h NodeInstallerProgressing: 1 nodes are at revision 12; 2 nodes are at revision 14
kube-controller-manager 4.14.16 True False False 23h
kube-scheduler 4.14.16 True False False 23h
kube-storage-version-migrator 4.14.16 True False False 22h
machine-api 4.14.16 True False False 22h
machine-approver 4.14.16 True False False 23h
machine-config 4.14.16 True False False 3h41m
marketplace 4.14.16 True False False 23h
monitoring 4.14.16 True False False 3h40m
network 4.14.16 True False False 23h
node-tuning 4.14.16 True False False 23h
openshift-apiserver 4.14.16 True False False 23h
openshift-controller-manager 4.14.16 True False False 23h
openshift-samples 4.14.16 True False False 23h
operator-lifecycle-manager 4.14.16 True False False 23h
operator-lifecycle-manager-catalog 4.14.16 True False False 23h
operator-lifecycle-manager-packageserver 4.14.16 True False False 23h
service-ca 4.14.16 True False False 23h
storage 4.14.16 True False False 23h
Take a look to the output above, and you will see that the etcd and the config-operator are already in the 4.15.28 version, and the kube-apiserver is in progress with some messages that allow to understand what is going on. This is very useful for troubleshooting.
Once the upgrade has finished we can review all the Clusters Operators in the intermediate version.
$oc get co
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE
authentication 4.15.28 True False False 24h
baremetal 4.15.28 True False False 24h
cloud-controller-manager 4.15.28 True False False 24h
cloud-credential 4.15.28 True False False 24h
cluster-autoscaler 4.15.28 True False False 24h
config-operator 4.15.28 True False False 24h
console 4.15.28 True False False 24h
control-plane-machine-set 4.15.28 True False False 24h
csi-snapshot-controller 4.15.28 True False False 24h
dns 4.15.28 True False False 24h
etcd 4.15.28 True False False 24h
image-registry 4.15.28 True False False 24h
ingress 4.15.28 True False False 5h18m
insights 4.15.28 True False False 24h
kube-apiserver 4.15.28 True False False 24h
kube-controller-manager 4.15.28 True False False 24h
kube-scheduler 4.15.28 True False False 24h
kube-storage-version-migrator 4.15.28 True False False 23h
machine-api 4.15.28 True False False 24h
machine-approver 4.15.28 True False False 24h
machine-config 4.15.28 True False False 5h11m
marketplace 4.15.28 True False False 24h
monitoring 4.15.28 True False False 5h11m
network 4.15.28 True False False 24h
node-tuning 4.15.28 True False False 76m
openshift-apiserver 4.15.28 True False False 24h
openshift-controller-manager 4.15.28 True False False 24h
openshift-samples 4.15.28 True False False 77m
operator-lifecycle-manager 4.15.28 True False False 24h
operator-lifecycle-manager-catalog 4.15.28 True False False 24h
operator-lifecycle-manager-packageserver 4.15.28 True False False 24h
service-ca 4.15.28 True False False 24h
storage 4.15.28 True False False 24h
Also we can review the Machine Config Pool to see that the Control Plane nodes are upgraded.
$oc get mcp
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE
master rendered-master-de736dc318ee0e73429b55e0673f0fbd True False False 3 3 3 0 24h
worker rendered-worker-25e7f5222944b2572fe43be49cdde9d0 False False False 2 0 0 0 24h
As you can observe the worker MCP is UPDATED False, but is not moving forward because the MCP is paused.
Let’s take a look to the nodes as well, to see that are in a newer version of Kubernetes.
$ oc get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master0.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 24h v1.28.12+396c881
master1.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 24h v1.28.12+396c881
master2.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 24h v1.28.12+396c881
worker0.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 24h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
worker1.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 24h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
In the last colum you can compare the Control Plane nodes version, with the previous one, now the Control Plane nodes are in v1.28.12+396c881.
At this point we can say that the Control Plane is upgraded to the 4.15.28. Let’s confirm that.
$ oc get clusterversion
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS
clusterversion.config.openshift.io/version 4.15.28 True False 20h Cluster version is 4.15.28
Update OLM Operators in intermediate version
Always, after upgrade the Control Plane, we have to upgrade the OLM Operators to keep it in the latest version for OCP 4.15.28. As we did before we have to review the install plan to be approved, and approve it to install the new version of MetalLB Operator.
$ oc get installplan -n metallb-system | egrep 'APPROVED|false'
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED
install-q9swk metallb-operator.v4.15.0-202408210608 Manual false
$ oc patch installplan -n metallb-system install-q9swk --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"approved":true}}'
installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-q9swk patched
At the moment of the upgrade we will see the Cluster Service Version(CSV) replacing the previous version and installing the new one.
$oc -n metallb-system get csv
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
metallb-operator.v4.14.0-202408081513 MetalLB Operator 4.14.0-202408081513 Replacing
metallb-operator.v4.15.0-202408210608 MetalLB Operator 4.15.0-202408210608 metallb-operator.v4.14.0-202408081513 Installing
When finished we will see only the new version of the CSV as Succeeded.
$oc -n metallb-system get csv
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
metallb-operator.v4.15.0-202408210608 MetalLB Operator 4.15.0-202408210608 metallb-operator.v4.14.0-202408081513 Succeeded
Acknowledge of changes between Kubernetes APIs
From the version 4.15 to 4.16 there are some removals in the Kubernetes APIs, so we have to ensure that all our workloads will run with the latest version of APIs used. This is responsibility of the administrator, there are several methods to identify if APIs are going to be removed are in use.
Once we are sure that our workloads are fine, we can unlock the upgrade to the 4.16
$ oc -n openshift-config patch cm admin-acks --patch '{"data":{"ack-4.15-kube-1.29-api-removals-in-4.16":"true"}}' --type=merge
configmap/admin-acks patched
Upgrade control plane to target version
Just launch the below command and monitor the Cluster Version, Cluster Operators and Machine Config Pools to see the upgrade process. Remember that you can also use the OpenShift Web Console to monitor the progress.
$ oc adm upgrade --to=4.16.8
Requested update to 4.16.8
Once the upgrade finished we should see the Cluster Version and the Cluster Operators all at 4.16.8 with healthy status.
$oc get clusterversion,co
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS
clusterversion.config.openshift.io/version 4.16.8 True False 113s Cluster version is 4.16.8
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING DEGRADED SINCE MESSAGE
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/authentication 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/baremetal 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/cloud-controller-manager 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/cloud-credential 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/cluster-autoscaler 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/config-operator 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/console 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/control-plane-machine-set 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/csi-snapshot-controller 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/dns 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/etcd 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/image-registry 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/ingress 4.16.8 True False False 18h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/insights 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/kube-apiserver 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/kube-controller-manager 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/kube-scheduler 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/kube-storage-version-migrator 4.16.8 True False False 18h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/machine-api 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/machine-approver 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/machine-config 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/marketplace 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/monitoring 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/network 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/node-tuning 4.16.8 True False False 45m
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/openshift-apiserver 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/openshift-controller-manager 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/openshift-samples 4.16.8 True False False 46m
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/operator-lifecycle-manager 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/operator-lifecycle-manager-catalog 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/operator-lifecycle-manager-packageserver 4.16.8 True False False 18h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/service-ca 4.16.8 True False False 19h
clusteroperator.config.openshift.io/storage 4.16.8 True False False 19h
Also we can check the status of the Machine Config Pools and the nodes.
$oc get mcp,nodes
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/master rendered-master-3828f7d90b01116701a48599b13b70ba True False False 3 3 3 0 20h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/worker rendered-worker-55695b99287955c613432d80bb75592d False False False 2 0 0 0 20h
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node/master0.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/master1.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/master2.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/worker0.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
node/worker1.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
We can observe that the master MCP is UPDATED True, and the worker MCP is UPDATED False, because it is still paused. Let’s move forward to update the OLM Operators.
Upgrade OLM Operators to target version
Always after upgrade the OpenShift Control Plane we have to upgrade the OLM operators, recall that we have the approval as Manual, in case that the approval on the operators is Automatic, this step will be performed automatically.
We are going to review which install plan need to be approved and approve it to install the newer version of MetalLB.
$ oc get installplan -n metallb-system | egrep 'APPROVED|false'
NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED
install-pbw8z metallb-operator.v4.16.0-202408262007 Manual false
$ oc patch installplan -n metallb-system install-pbw8z --type merge --patch '{"spec":{"approved":true}}'
installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-pbw8z patched
After a while we can check the status of the CSV to see if the operator has been upgraded successfully.
$ oc -n metallb-system get csv
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
metallb-operator.v4.16.0-202408262007 MetalLB Operator 4.16.0-202408262007 metallb-operator.v4.15.0-202408210608 Succeeded
Unpause worker MCP
Great! we are almost done, we just need to upgrade the worker nodes, because at this point we have on 4.16.8 only the Control Plane of our cluster and the OLM Operators, but the nodes where our workloads are running are still in the 4.14.16.
Before unpause the worker MCP we are going to check the value of maxUnavailable. This value define the amount of nodes that can be down in the cluster and our workloads will be not affected. By default the value es 1 and if it is not defined, as we can see bellow, that means that we are going to upgrade one by one the nodes of this MCP.
$oc get mcp worker -ojsonpath='{.spec.maxUnavailable}'
$
Now we can unpause the worker MCP.
$oc patch mcp/worker --patch '{"spec":{"paused":false}}' --type=merge
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/worker patched
What happen now is that the Machine Config Operator will install the newer version of RHCOS on the two worker nodes. This action require the nodes to be rebooted, and will be done one by one, because we ensured that the maxUnavailable was by default to 1.
This process can take a while, and depending of the number of nodes can be a very long process, in this case we have only two nodes. Also if we have more nodes and our workloads are defined to allow multiple nodes to be down at the same time, we can increase the value of maxUnavailabe to a percentage or a number, and the upgrade will be done by chunks.
Let’s review the status of the MCP and nodes.
$oc get mcp,nodes
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/ht100gb rendered-ht100gb-16b3a1d32da74161b66bd9a59e35a245 True False False 0 0 0 0 20h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/master rendered-master-3828f7d90b01116701a48599b13b70ba True False False 3 3 3 0 20h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/standard rendered-standard-16b3a1d32da74161b66bd9a59e35a245 True False False 0 0 0 0 20h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/worker rendered-worker-55695b99287955c613432d80bb75592d False True False 2 0 0 0 20h
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node/master0.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/master1.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/master2.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/worker0.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
node/worker1.ocp1.r450.org NotReady,SchedulingDisabled worker 20h v1.27.10+c79e5e2
If you review the output above you will see that the worker1 is rebooting at this moment, because is NotReady, and it is still in the previous version. We can keep the above command with a watch to see in real time how is progressing. For convenient the next capture will be when the process is finished, and check that the two worker nodes are in the target version.
$oc get clusterversion,mcp,nodes
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS
clusterversion.config.openshift.io/version 4.16.8 True False 70m Cluster version is 4.16.8
NAME CONFIG UPDATED UPDATING DEGRADED MACHINECOUNT READYMACHINECOUNT UPDATEDMACHINECOUNT DEGRADEDMACHINECOUNT AGE
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/ht100gb rendered-ht100gb-16b3a1d32da74161b66bd9a59e35a245 True False False 0 0 0 0 21h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/master rendered-master-3828f7d90b01116701a48599b13b70ba True False False 3 3 3 0 20h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/standard rendered-standard-16b3a1d32da74161b66bd9a59e35a245 True False False 0 0 0 0 21h
machineconfigpool.machineconfiguration.openshift.io/worker rendered-worker-96e7b44c25d7ea5d601f63211fa2f40b True False False 2 2 2 0 20h
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node/master0.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/master1.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/master2.ocp1.r450.org Ready control-plane,master 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/worker0.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
node/worker1.ocp1.r450.org Ready worker 20h v1.29.7+4510e9c
So that’s it, we have our cluster upgraded to 4.16.8. Also we can review the Web Console on the left menu Administration > Cluster Settings
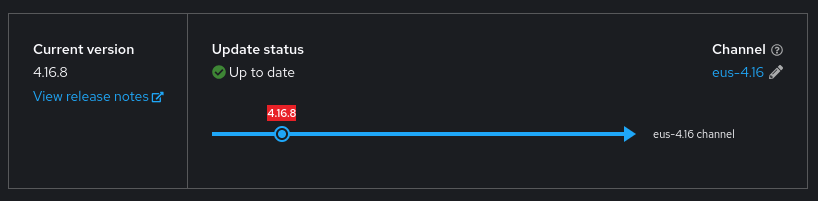
Summary
We have explained what is an EUS version and why it is useful for production clusters, and describe a procedure on how to perform the upgrade on a baremetal cluster, taking in account a lot of manual steps for a better understanding of the process, but most of those can be automatic.
It is important to highlight how OpenShift helps to upgrade a cluster in a more consistent way as a custom Kubernetes deployment, because take in account the OS version on the nodes and handle the Kubernetes components like operators, making the process more consistent. Moreover we have described how to update our cluster to avoid a break in the services of our workloads, upgrading first the Control Plane, and afterward the worker nodes where our workloads are running, and do that by chunks to allow the cluster to reschedule pods running on the nodes that are being rebooted for the upgrade.
